The Anaconda Plan, is the (retrospectively) un-ironic name given to the much modified but eventually successful Federal Grand Strategy to win the Civil War.
The (very) rough outlines of the plan were sketched out by U.S. Army General-in-Chief Brevet Lieutenant General Winfield Scott in May of 1861.

General Scott envisioned a grand envelopment (a crushing Anaconda in the public mind) which would divide, isolate, and economically cripple the seceded states. Scott wished to avoid a “war of conquest” if possible, so he called for a naval blockade to isolate the seceded states from foreign markets and imported goods. His main military action was to be a huge offensive down the Mississippi River, seizing key points along this strategic artery to put in under Federal control all the way down to the Gulf of Mexico.
“The object being to clear out and keep open this great [riverine] line of communication in connection with a strict blockade of the sea-board, so as to envelope the insurgent States and bring them to terms with less bloodshed than by any other plan.” [LTG Winfield Scott letter to MG George McClelland, May 21, 1861]
Scott did not wish to have to force the “insurgent States” back into the Union as “conquered provinces”, and he believed that there was significant “latent Unionism” in the seceded states which might be rekindled (a view Lincoln shared at the time). Isolation from foreign markets, a drought of luxuries, and economic collapse might, in Scott’s mind, bring many of the insurgents back into the U.S. with a minimum of destruction.
At the time Scott’s concept was widely derided. The label “Anaconda Plan”…or “Scott’s Great Snake”….came from enemies of the Plan, or of the Administration. Unionist fire-brands who supported a more direct “on to Richmond” strategy dismissed it as passive and weak. Peace Democrats and Confederate commentators dismissed it as doomed to fail, and as foolishly underestimating Confederate determination to break away.
In the end, Scott DID underestimate the Confederate will to fight and willingness to accept privation to achieve independence. The Confederate population proved willing to not only forgo luxuries, but bore up under economic collapse and serious food shortage. Still, Scott was right that the blockade would be a key to victory, and that a long complex campaign on the Mississippi (far from the dueling capitals) would be vital to eventual success.
Scott also saw something that few did at the time: that it would be a hard, LONG war. At the time of the plan’s origination, most Federal volunteer troops were “Three Months Volunteers”, mustered for 90 days service under the Militia Act of 1795. Scott had little use for the Three Months Men, as they could hardly be armed and partially trained before them would be mustered out. His main hope for these short-term volunteers was that they might receive some military instruction during that period, so they could be more useful as recruits for future “Three Year Regiments”. At the time, many commentators, North and South, still believed the war would be over in a matter of months.
Scott’s plan for the (Anaconda-like) slow crushing of the Confederate economy, was eventually put into place, although with the addition of the conquest and attrition Scott hoped to avoid.
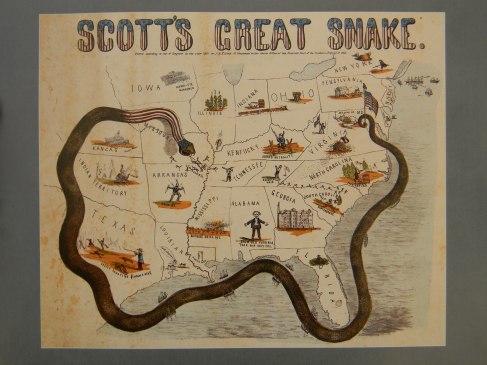
The wonderful graphic of “Scott’s Great Snake” presents a great Federal “Anaconda” …studded with Navy ships…..wrapping around the southern states, and curling around to plunge, snake head-first down the Mississippi. It was created by J. B. Elliott of Cincinnati in 1861.
But in addition to the Great Snake there are numerous other miniature images, often commenting on current (to 1861) views of states or recent events. The snake’s tail is anchored to an American Flag at Washington, topped with a liberty cap.
A enthusiastic zouave, in puffy red pants, charges out of New York, as a winged helmet emblazoned “Free Trade” hovers overhead.
Maryland declares “We give in” as a bridge burns on the MD/VA border.
A West Virginian defends “The Old Flag” with a sword, as the rest of Virgina is symbolized by a battered bee hive, topped with a tattered Confederate Flag [First National pattern] hanging from a broken staff.
A North Carolinian notes that pine rosin is “Poor Eating”, while “Contrabands” escape slavery in South Carolina.
The Georgian cotton factory is abandoned and wrecked, while a lone Floridian sits in a swamp.
A proud Alabamian is angry that “Dam old Virginai took our Capitol”, because the CSA capitol was transferred from Mongomery, AL to Richmond. 😦
Some of the cartoons are grim or horrible. Rebelling slaves (apparently) are “burning massa out” as a plantation burns. In Louisiana a “Union Man” is hung while locals complain that they can’t ship out their cotton. Next door in Texas a planter shoots fleeing slaves, noting it is “costly shooting $100,000 a head”
Kentucky….wearing a coonskin cap…. perches on the fence, trying to maintain “Armed Neutrality”
Tennessee is divided, with the Unionist “Knocksville [Knoxville] Whig” [Newspaper] leading East Tennesseans in defending the American Flag. In West Tennessee a secessionist in a cocked hat looks for threats across the Mississippi.

There, the Great Snake is chasing out Missouri’s secessionist Governor, Claiborne Fox Jackson (the fleeing jackass), while an over-armed Arkansan wields two Bowie Knives and wearing two muskets over his shoulders.
A native chief smokes a pipe in Indian Territory [Oklahoma today], while in “Kanzas”, marching feet make “Union Music”. A second battalion of “Hawk-Eye Marksmen” march south, while a cannon points south from the Federal redoubt at Cairo [pronounced Kay-Roh] Illinois, where Ft Defiance guards the junction of the Ohio and the Mississippi.
A detailed examination of “Scott’s Great Snake” can be made at the Library of Congress:
http://memory.loc.gov/cgi-bin/map_item.pl?data=/home/www/data/gmd/gmd370/g3701/g3701s/cw0011000.jp2&style=gmd&itemLink=r?ammem/gmd:@field%28NUMBER+@band%28g3701s+cw0011000%29%29&title=Scott%27s%20great%20snake.%20Entered%20according%20to%20Act%20of%20Congress%20in%20the%20year%201861%20by%20J.B.%20Elliott%20of%20Cincinnati.









Recent Comments